Diverticulitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of intestinal diverticula. Understand this problem and clear your doubts in this article developed by the EndoBlog team.
Diverticula are like small pouches that project out from the lining of the intestine.
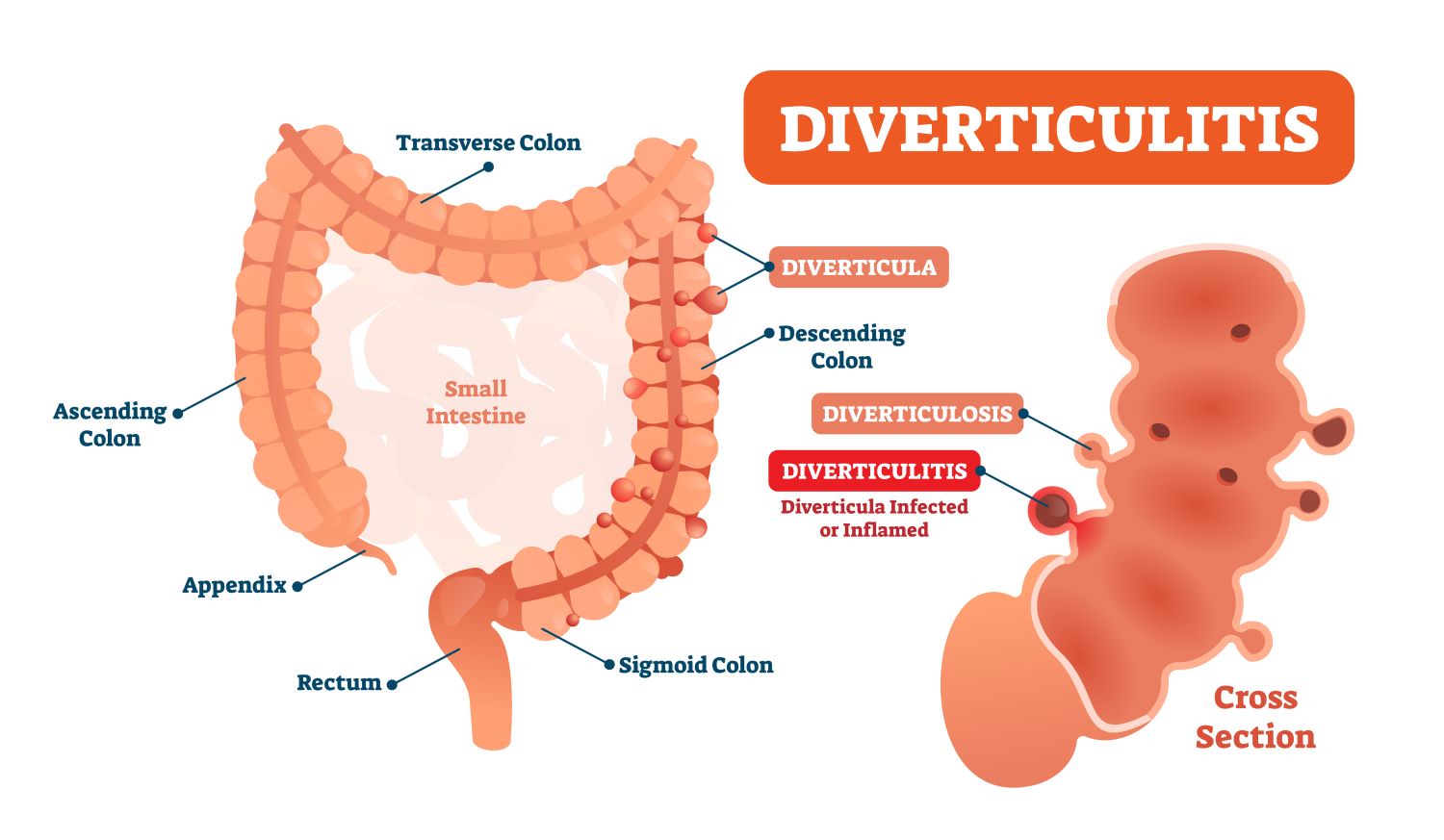
The propensity to develop diverticula occurs as a person ages. Approximately, one-third of the population over 50 and two-thirds over 80 develop the condition.
See more at: Intestinal Diverticula: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Important: the mere presence of diverticula in the intestine corresponds to a condition called diverticulosis. When they become inflamed, they are diagnosed with diverticulitis.
What are the symptoms of diverticulitis?
Most patients with intestinal diverticula do not present symptoms of diverticulitis. The diverticula alone do not cause symptoms and are diagnosed by exams done to analyze some other abnormality in the intestine.
However, sometimes, a diverticulum can become inflamed and cause symptoms, such as:
- abdominal pain, mainly in the lower left side of the belly, which can be constant and persist for many days;
- chills;
- nausea, nausea, and vomiting;
- fever;
- loss of appetite;
- periods of constipation or diarrhea;
- blood in the stool, in some cases.
How is diverticulitis treated?
In milder cases of diverticulitis, treatment involves a balanced, more liquid diet, as well as the prescription of antibiotics and painkillers. In some cases, when, for example, the pain is very intense and there are signs of widespread infection, hospitalization is necessary for the application of intravenous antibiotics and clinical management.
If the patient does not respond well to preliminary treatment, there are two approaches: drainage of abscesses, through percutaneous puncture, or surgery to remove the portion of the intestine affected by diverticula. The alternatives for procedures depend on the severity of the condition, and in cases of intestinal perforation, emergency surgery must be performed.
Important: diverticulitis is a condition that tends to have frequent recurrences, so surgery may be necessary after recurrent episodes.
Is it possible to prevent diverticulitis crises?
Although there are no completely effective measures to prevent crises, some things can be done to help, for example:
- drink plenty of water;
- perform physical exercises as recommended by the doctor;
- observe possible changes in bowel function. Constant diarrhea or constipation requires a consultation with the doctor;
- follow the treatment as directed by the doctor, which includes changes in eating habits;
- after recovering from a crisis, it is necessary to have a lighter diet, with foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables;
- the recommendation to avoid foods with seeds is controversial, as scientific studies cannot prove this direct relationship. However, it is prudent to avoid the following foods: popcorn kernels, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, and nuts, as they can cause pain by getting trapped in diverticula.
Important: cucumber seeds, tomato, zucchini, raspberries, strawberries, and poppy seeds are usually harmless for those suffering from diverticulitis.
Learn more about diverticulitis and the digestive system through EndoBlog
To get true and quality information about diverticulitis, other conditions that affect the digestive system, and general exams, such as digestive endoscopy, follow the content developed by the EndoBlog team.
EndoBlog is a portal conceived by a team of gastroenterology specialists with the purpose of providing true information, given by doctors, so that the population has a full understanding of the topic.
Browse the site and follow all the content from EndoBlog.
